Knee pain is a very annoying disorder that, unfortunately, most people face. They can be sharp, painful, burning, throbbing, limit joint mobility, present only during physical activity, or even during rest. But many, instead of going to the doctor, try to get rid of it with the help of painkillers, especially ointments, gels or tablets of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Such drugs, although they have anti-inflammatory properties, are unable to influence the pathogenesis of knee pain, and therefore only temporarily contribute to their elimination. Therefore, they can only be considered as a method of symptomatic therapy.
But the cause of discomfort in the knee joint can lie in the occurrence of various disorders, both directly in the knee, and in the spine or other parts of the body. Therefore, it is possible to develop effective treatment strategies that will really help relieve pain only after determining the true cause of their appearance. To do this, you will need to undergo a series of diagnostic procedures and seek expert advice, but this is the only way you can truly improve your well-being and prevent the development of complications.
cause
Pain in the knee can accompany a variety of diseases, ranging from arthrosis of the knee joint to pathology of the lumbar, sacral spine, and pelvic bones. Also, the cause of discomfort or acute pain in the knee can be chondropathy, arthritis, neuritis and other similar diseases.
The obvious causes of the development of pain syndrome are injuries of various types from bruises, dislocations, ligament ruptures, damage to the meniscus or intra-articular fractures. But in such situations, the pain is almost always acute and appears at the time of impact, fall or other traumatic factors. Therefore, in such cases, the victim should contact a traumatologist to treat the consequences of the injury.
Thus, pain in the knee is always a sign of a pathological process affecting the structure of the cartilage, bone or soft tissue of the knee itself, or damage to the nerves that invade it. Consider the main reason for their appearance.
Arthrosis of the knee joint or gonarthrosis
Osteoarthritis, osteoarthritis of the knee or gonarthrosis is one of the most common causes of knee pain. The disease is characterized by the occurrence of degenerative-dystrophic processes in the cartilage structure of the joints, which are the result of violations of the flow of metabolic processes, the action of traumatic factors in the past, etc. Often, gonarthrosis is diagnosed in middle -aged and elderly people, athletes and people engaged in heavy physical labor.
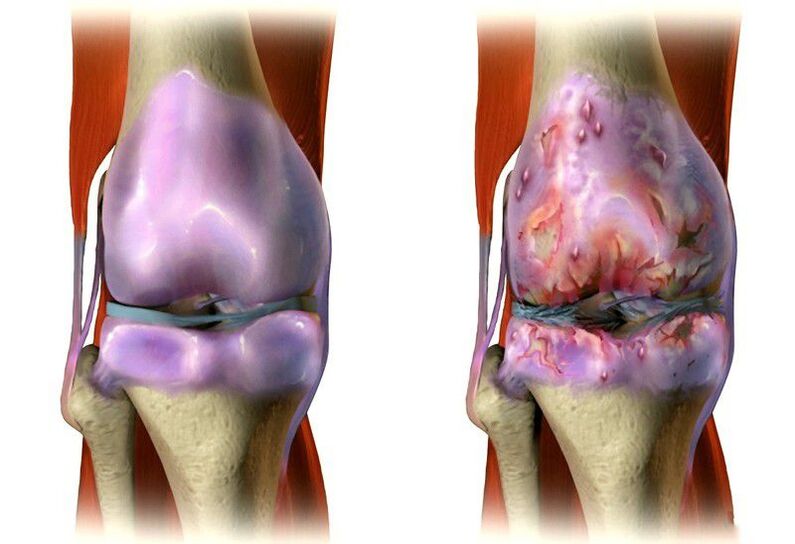
The disease has a chronic course, tends to develop slowly and eventually leads to obvious limitations of joint movement, violation of limb support function (often both), as well as pain. At first, they are dull, painful, interesting in nature and appear during movement, accompanied by cramps in the knees, especially while climbing stairs. But in the absence of treatment, the cartilage of the knee joint continues to wear out gradually, leading to an increase in pain and its presence even at rest. Thereafter, destruction of the articular surface occurs, which exacerbates the condition and can even lead to deformity.
A special feature of arthrosis of the knee joint is the presence of initial pain, for the elimination of which the patient needs to "disperse". Thanks to this, an improvement is observed within 15-30 minutes.
Gonarthrosis is often complicated by the addition of inflammatory processes that can affect synovial bags, ligaments and tendons. This leads to a sharp increase in pain, acquisition of a ruptured character, swelling of soft tissues and an increase in local temperature.
Spinal disease and pelvic bone asymmetry as causes of knee pain
At first glance, there is no connection between the lumbar spine and the knee. But in reality this is not so. They are closely linked by the sciatic nerve (nervus ischiadicus), which is the main nerve of the foot. It originates in the spine and is formed simultaneously by fibers that extend from the spinal cord through natural openings in the nerve vertebrae:
- L4;
- L5;
- S1;
- S2;
- S3.
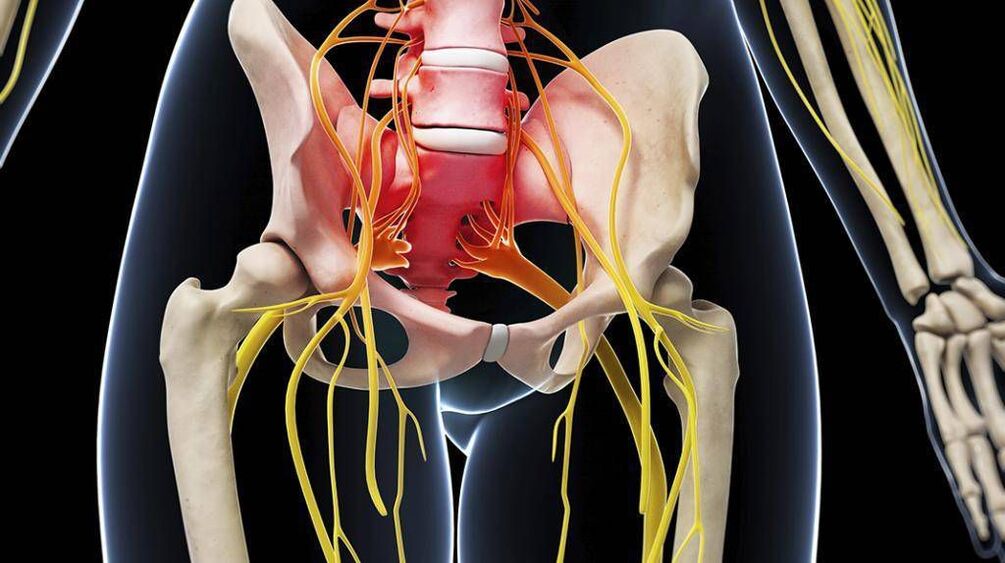
These nerves pass through the vertebrae of the same name, uniting at the level of the sacrum into the nerve plexus. From it, the sciatic nerve departs along the dorsum of each leg and invades the knee. At the same time, these nerves are responsible for sensitive (sensory) and motor (motor) functions. Thus, a violation at any point of its passage, particularly at the level of the lumbar region, can trigger the appearance of pain in the knee. Often it is associated with the development of:
- Osteochondrosis, protrusion and intervertebral hernia. The disease is based on degenerative-dystrophic changes in the intervertebral disc located between almost all vertebrae. They are characterized by a systematic decrease in the height of the disc and its dehydration, which leads to a decrease in the elasticity of the structure and an increased risk of its rupture under load. As a result, the vertebrae move closer to each other, which can cause compression of the nerve roots that pass through them. If such changes occur in the lumbar region, compression of the fibers that make up the sciatic nerve is possible and, thus, the appearance of pain in the knee. But more often these symptoms occur when osteochondrosis is complicated by the formation of protrusion (protrusion) of the intervertebral disc or its hernia (rupture of the outer shell of the disc), because the protruding area can compress the spinal roots strongly directly in the spinal canal and give rise to severe neurological complications. , including pain in the knee.
- Spondylosis. This is the disease that most often develops with a background of osteochondrosis and chronic. Thus, there is excessive growth of the vertebral body surface adjacent to the intervertebral discs, and the formation of bone protrusions (osteophytes) on them. In severe cases, neighboring vertebrae can grow together, leading to immobilization and severe compression of the nerves that pass through it.
- Spondylolisthesis. The term refers to the pathology of the spine, in which the vertebrae above it are moved in relation to those located below it. Often, the lumbar region is affected, leading to a violation of the nerves that make up the sciatic nerve.
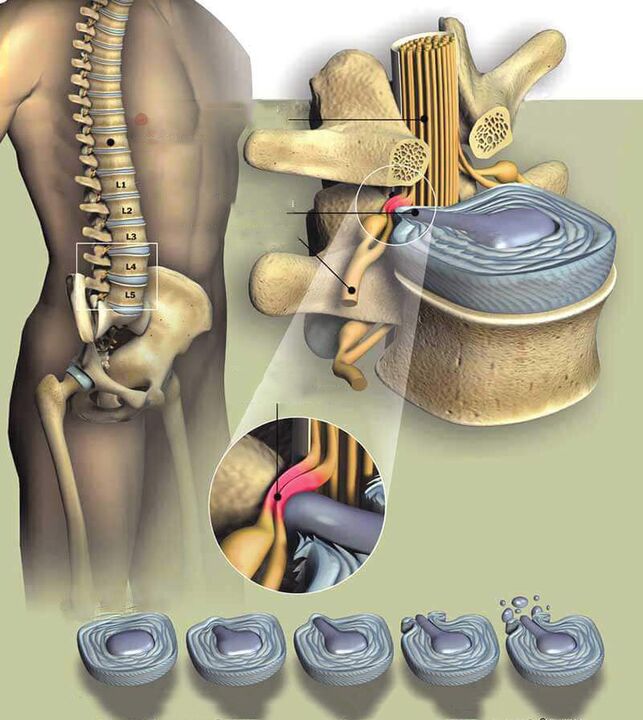
Signs in which one may suspect the cause of the development of pain in the knee as a result of the occurrence of lumbar spine pathology may include:
- pulling, aching, sharp pain in lower back;
- muscle tension, hamstrings, quadriceps femoris, occupying the entire anterior surface of the thigh and partly the outer part;
- pain and stiffness in the hips;
- pervasive pain in the legs;
- pain in the upper thigh.
In each case, the set, nature and severity of symptoms will be different. This largely depends on the individual characteristics of the organism and the degree of nerve compression.
Directly on the defeat of the sciatic nerve can show (symptoms can be observed only in one limb, and in both at once):
- pain in the knees, hips and lower back;
- back and leg muscle spasms;
- burns on the back of the legs;
- loss of control over bladder and intestinal function.
With a violation of the function of the sciatic nerve, there is often a feeling of instability in the knees, their compression. As a result, the patient complained that he could not rely entirely on his feet.
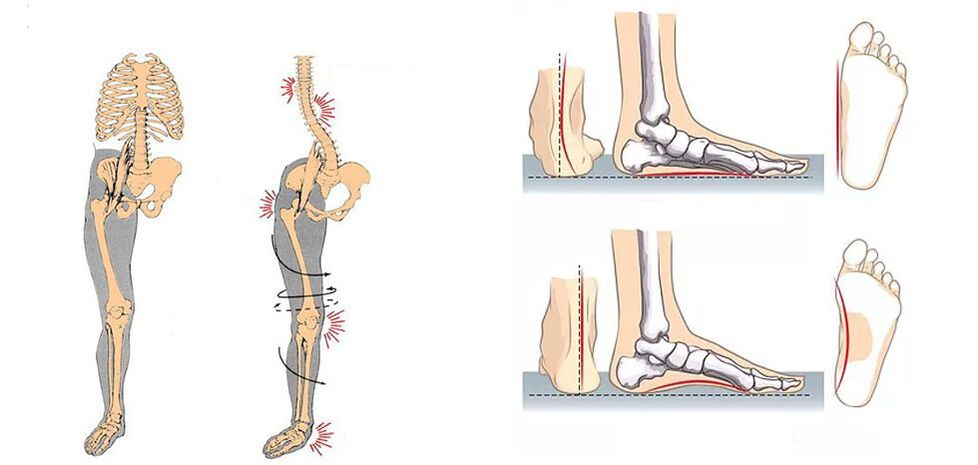
Asymmetry of the sacrum and pelvic bones can also trigger the appearance of pain in the knee joint. It occurs as a result of differences in the length of the lower legs, which may be due to congenital features or curvature of the pelvis, including with a background of scoliosis. This leads to excessive load on one leg and faster wear of the cartilage of the knee joint, resulting in arthrosis.
The abdominal muscles, which are attached to the pubic bone, are responsible for ensuring the stability of the pelvic bones. When they are weak due to being overweight, leading an inactive lifestyle, or other factors, the muscles of the back of the thighs become overburdened. This in turn puts an excessive strain on the knee joint.
Foot and ankle pathology
The ankle joint, as well as the knee, can be affected by arthrosis. Often it is diagnosed in athletes, especially ballet dancers, gymnasts, as well as in the elderly. This leads to a violation of the biomechanics of movement, which increases the load on the knee joint and contributes to its faster wear. In such a situation, a person will be bothered by pain not only in the knees, but also in the ankles, which significantly affects the gait due to limited movement.
Foot pathology, particularly flat feet and hallux valgus, can also trigger an increase in load on the knee and cause pain in it. This orthopedic pathology is very common today and in most cases begins to form in childhood, and worsens in adulthood. Valgus deformity is characterized by a violation of the axis of the ankle joint due to the collapse of the foot inwards. This is associated with increased leg fatigue, pain in them, but in turn can cause pain in the knee.
Diagnostics
If you experience pain in the knee, especially if it occurs frequently or is always present, you should see a doctor. If a patient has recently experienced a traumatic factor, he or she should contact an orthopedic traumatologist. In other cases, you can initially sign up for a consultation with a therapist. The doctor will assess the patient’s condition, collect anamnesis and prescribe diagnostic procedures. This will allow him to make an early diagnosis and refer the patient to a specialist whose help will be most effective in a particular case.
But you can immediately contact a neurologist if a person notices the presence of lower back pain, diffuse pain in the legs, burning on the surface of his back, or other symptoms mentioned above. This will save time and money, as soon as possible to determine the real cause of changes in well -being and start treatment. If the patient notices a change in the condition of the foot, in addition to pain in the knee, he is worried about pain in the ankle joint, it is better to immediately make an appointment with an orthopedic specialist.
In any case, the doctor will review the situation in detail, assess the nature of the complaint and refer the patient for examination, which may include:
- laboratory tests (UAC, biochemical blood tests) required to identify signs of inflammatory processes occurring in the body;
- x-rays of the knee in two projections (with suspected pathology of the legs or spine, they are also examined using radiography), which are necessary to assess the state of bone structure, as well as to identify indirect signs of a number of diseases;
- CT is used for a more accurate diagnosis of joint diseases, as well as the most reliable assessment of their degree of destruction;
- Ultrasound of the knee joint, used for visual assessment of all knee structures, their size, position;
- MRI, which is currently the best method for diagnosing various pathologies of soft tissue structures, including cartilage of the knee joint and intervertebral discs.
In some cases, patients may be given arthroscopy, which is an invasive method for diagnosing and treating knee joint pathology. As a rule, it is required for severe arthrosis and traumatic injuries of the ligaments, menisci, etc.
Treatment
Since there are many diseases that can manifest as pain in the knee, there is no single treatment strategy. In each case, it is developed individually, based solely on the nature of pathological changes, their severity, the presence of corresponding pathology, individual characteristics of the patient, his age, etc.
In cases of spinal pathology that causes pain in the knee, treatment is carried out under the supervision of a neurologist. If they are the result of arthrosis, other pathologies of the knee, ankle joints, feet, treatment is prescribed by an orthopedic specialist.
When diagnosing pathology of the spine or pelvic bones, the patient, in addition to consulting a neurologist, may also be recommended to visit an endocrinologist who will help solve the problem of excess weight.
All patients with spinal diseases, orthopedic pathology, including arthrosis of the knee joint, are shown complex treatment, which may include:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- exercise therapy;
- manual therapy.
Each measure was selected strictly individually according to the diagnosis and the degree of neglect of the pathological changes. And with 2-3 degree knee joint arthrosis, plasmolifting is often also prescribed.
Medical therapy
Drug treatment usually includes 2 areas: symptomatic and etiotropic therapy. The first aims to quickly improve the patient’s well -being, eliminating knee pain and other pre -existing symptoms. The second goal is a direct effect on the cause of the development of the disorder and the normalization of the patient's condition in the long run.
Therefore, in most cases, patients are prescribed drug complexes:
- NSAIDs are symptomatic therapies that allow you to quickly stop pain in the knees, lower back, legs and have anti-inflammatory effects.
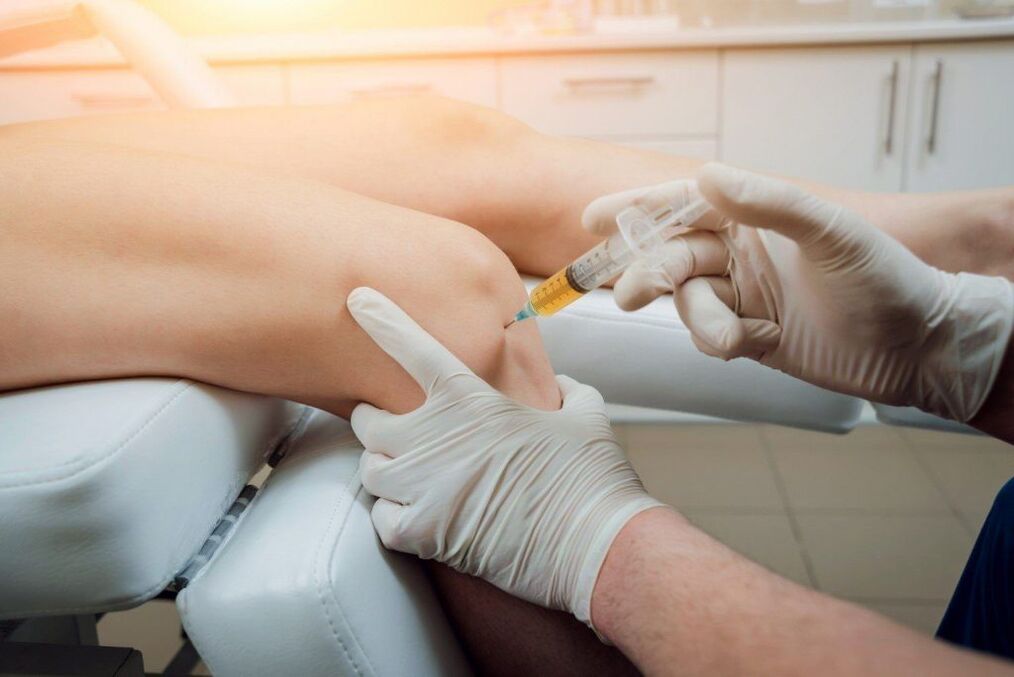
- Corticosteroids are drugs with strong anti-inflammatory effects, indicated for severe inflammation and most often injected into the joint cavity. It is used in short courses.
- Chondroprotectors are products that contain components used by cartilage tissue for regeneration. They are appointed by a long course, the duration of which is usually at least 2-3 months.
- Muscle relaxation is a medication prescribed for back and hip muscle spasms, which are often the body’s reflex response to pain impulses.
- Vitamin complexes are drugs that have been shown to improve the course of metabolic processes in the body, as well as the transmission of bioelectric nerve impulses along nerves.
Plasmolifting
Plasmolifting is the injection of plasma obtained from a patient’s own blood directly into the affected knee joint or the soft tissue around it. Due to the saturation of blood plasma with platelets, cytokines and growth factors, it contributes to:
- stimulation of the flow of natural regeneration processes;
- restoration of normal composition and amount of synovial fluid;
- activation of blood circulation and nutrition of joint cartilage;
- elimination of inflammation;
- pain relief;
- restoration of normal range of motion in the affected joint;
- reduction of treatment time by 2-3 times.
PRP-therapy, also called plasmolifting, perfectly complements the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint, so it is often included in the treatment regimen for this disease. It can also be used in the treatment of spinal osteochondrosis and injuries, complementary drug therapy, physiotherapy, exercise therapy and other treatment methods.
Physiotherapy
For the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system that cause pain in the knee, various types of physiotherapy procedures can be used. They increase the effectiveness of other treatments and have a positive effect on the affected area. Physiotherapy is always prescribed in a course of 7-15 procedures, selected individually. Often they seek help:
- magnetotherapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- UHF;
- phonophoresis;
- electrophoresis;
- SMT therapy or amplipulse therapy;
- vibration massage.
exercise therapy
Physiotherapy training plays an important role in the treatment of joint pathology of any localization and the spine in particular. It allows you to increase the range of motion in a dosing manner, as well as stimulates blood circulation, which leads to the nutritional activation of all structural elements of the knee joint and thus contributes to their regrowth.
But it is important to choose the optimal set of exercises that will be most useful in this situation and will not cause harm. Patients may be advised to do stretching exercises, which are very important for spinal pathology. Also, exercise is almost always prescribed to strengthen the musculoskeletal system. They contribute to the formation of a strong muscular skeleton, which will reduce the load on the affected joints and create favorable conditions for their recovery.
Physical therapy classes are convenient and accessible to all ages, as individually designed programs ensure the creation of dosing loads that have a positive effect on diseased joints, and exclude potentially harmful exercises. But to master the methodology of each of the proposed exercises as accurately as possible, it is worth conducting the first class under the supervision of an exercise therapy instructor.

In the future, you can practice at home, in nature or in any other suitable place, but every day. Systematics is one of the basic rules for the success of physiotherapy training. Therefore, it must be added to your list of daily activities and given the appropriate amount of time - 20-30 minutes is usually enough. During class, it is important to avoid sudden and hurried movements, as this can cause pain and worsen the condition.
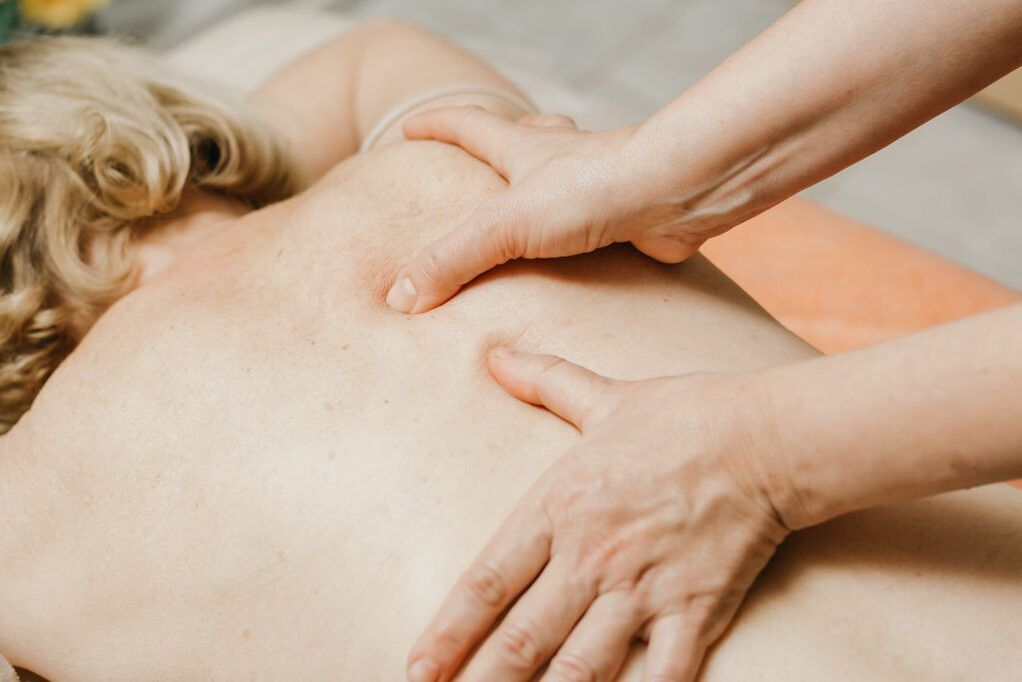
Manual therapy
Manual therapy plays one of the major roles in the correction of pelvic asymmetry and the treatment of spinal diseases. It involves an in -depth study of the back muscles, ligaments and joints of the spine, the pelvic area by the hands of a specialist. There are many methods and techniques of manual influence. They are selected depending on the type and severity of the existing pathology.
Thanks to the course of manual therapy sessions, it is possible to:
- eliminating back pain by relieving pressure on nerve fibers;
- improve the nutrition of all spinal structures due to the activation of blood circulation;
- increase spinal mobility;
- improve posture by eliminating spinal deformities;
- restores the normal position of the pelvic bones and internal organs, which has a positive effect on its function.
But the most important effect of manual therapy for patients who consult a doctor with knee pain is the removal of compression of the sciatic nerve and the fibers that make it up. This leads to a progressive improvement in the condition and the elimination of pain syndromes, as well as other neurological disorders.
The patient saw the first positive change after the first session. The procedure further contributes to its growth and stabilization for a long time. The first procedure can be carried out only after the removal of acute inflammation with the help of drug therapy, physiotherapy and other methods of treatment.

Thus, pain in the knee may indicate not only its defeat, but also the occurrence of problems in other parts of the musculoskeletal system, in particular the spine and legs. In any case, they should not be ignored, because pre -existing pathologies, in the absence of competent treatment, tend to develop over time. This will lead to an increase in the severity of pain, the occurrence of other unpleasant symptoms and, in general, a decrease in the quality of human life. Therefore, if discomfort appears on one or both knees, you should see a doctor: an orthopedist or a neurologist. Timely treatment in the early stages of the development of pathological changes will allow you to reverse them and fully restore the normal function of the joints, ensuring freedom of movement for many years.































